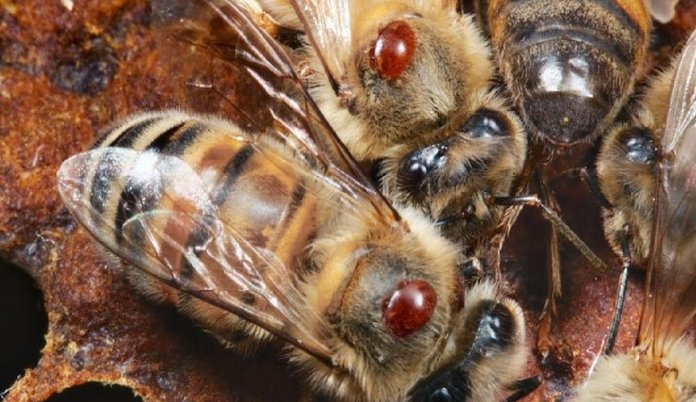

The tick of varroa was discovered by scientists in the early 20th century, but a colossal spread began in the middle of the last century.
The female tick is able to live up to 10 months, the male is only 5-15 days.
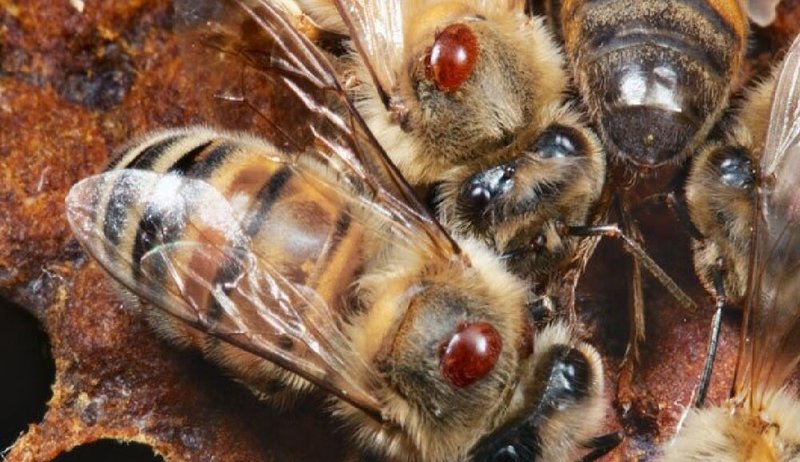

Over the entire period of her life, the female is able to postpone up to 40 generations of the tick. The development of the tick in the family occurs with a geometric progression and phenomenal speed. If the beekeeper does not take measures to combat this parasite, in 1-2 years you can completely lose the apiary.
A few facts about the tick of varroa:
The female tick enters the bee cell 1-3 days before the seal, lays 3 to 5 eggs in it. Typically, the first male egg.
The male does not feed on the hemolymph of the bees; he does not feed on anything. His task is to impregnate the female sisters, after which he dies.
Hatching from eggs and fertilized females attach to the bee. It is worth noting that not all females survive. They often die choking in the stern, which the larva has not eaten, and become entangled in the cocoon that it will come.
Females who still managed to survive safely leave the cell, like brave riders on a young bee.
Females are able to move not only in the bee itself, but also from bee to bee. In addition, many of them often leave the hive with the flying bee, thus apiary regeneration occurs.
As a temporary stay, the tick can parasitize on bumblebees, wasps and even flies. Able to make temporary stops at flowers and drinking bowls, he can wait 5 to 7 days to wait for his victim!
What should the beekeeper do?

In connection with such a colossal tick migration, especially for nomadic beekeepers, we are forced to adapt to modern realities.
Already not enough treatment in the fall at the end of the season, as it was 30-40 years ago. Treatments should be approached comprehensively, throughout the year, only winter is an exception, and the period of active honey collection.
Do not forget that a tick may develop immunity to a particular drug. therefore beekeepers are forced to constantly change the active substance, the medicine that is used, as well as the technology for its delivery.
3 main ways to deal with ticks
At the moment, there are 3 ways to effectively deal with ticks, this is zootechnical, chemical and acid.
There are 4 ways - this is the use of various essential oils. I do not regard this method as a serious cure for a tick. The maximum that essential oils are capable of is to some extent resist the apiary re-conditioning. However, I have not seen any serious research and scientific evidence on this subject. (If you know more about this issue, forgive me in the comment!)
Zootechnical method - rather weak
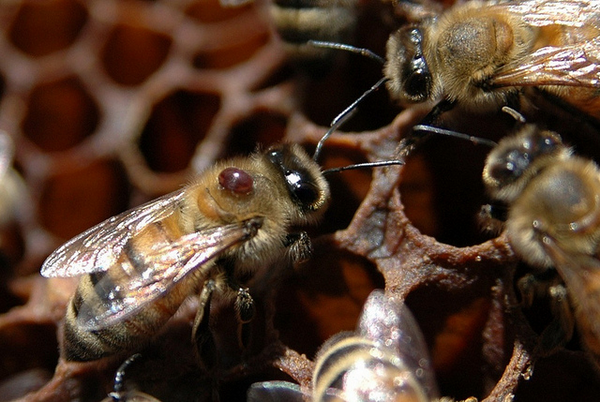

Concerning zootechnical method, it is based on the fact that the female tick prefers to lay eggs in the drone brood rather than in the bee.
This is due to the temperature difference during ripening. The beekeeper simply sets up a building frame in the brood area. Bees willingly rebuild drone cells, and the uterus sows them. When the drone larvae are sealed, the beekeeper extracts this frame and cuts out the dry land with brood and tick, then returns the frame back, and as they say: our song is good, start over ...
My recent observations have shown that the modern tick has adapted to this. Its greatest number is now found not in the drone, but in the bee brood. therefore If you decide to use the zootechnical method of combating ticks, I advise you to do this in combination with other methods of treatment.
The acidic method is good and safe, but only suitable for the warm season
The second most popular way to fight is acid. For this, there are three main types of acids: lactic, formic and oxalic, which beekeepers have been successfully using for many years.
There are different ways of supplying acids: by sublimation with smoke, by usual pouring an acid solution, and the most modern way at the moment is sublimation of oxalic acid.
If you are fighting for the environmental friendliness of those beekeeping products that you receive, the use of acids will help you with this. There is only one drawback, any of these acids works when the average daily temperature is not higher than 18-20 degrees.
Chemical - the most effective, but there may be negative consequences
But the weather can’t be ordered, so comes to the rescue chemical tick control method. There are many chemicals, but the main active ingredients, only a few. These are thymol, amitrase and fluvalinate.
The most harmless of all of these is amitrase.
After application, it breaks down into components within a day. What can not be said about fluvalinate, which can be found in wax and honey even after 10-20 years! Therefore, if you have chosen the chemical method for yourself, I advise you to carefully familiarize yourself with the drug used.
The chemical processing method has the right to exist, just take it seriously and apply it only when it is possible and does not harm the final product.


























